What are the characteristics of magnesium alloy profiles
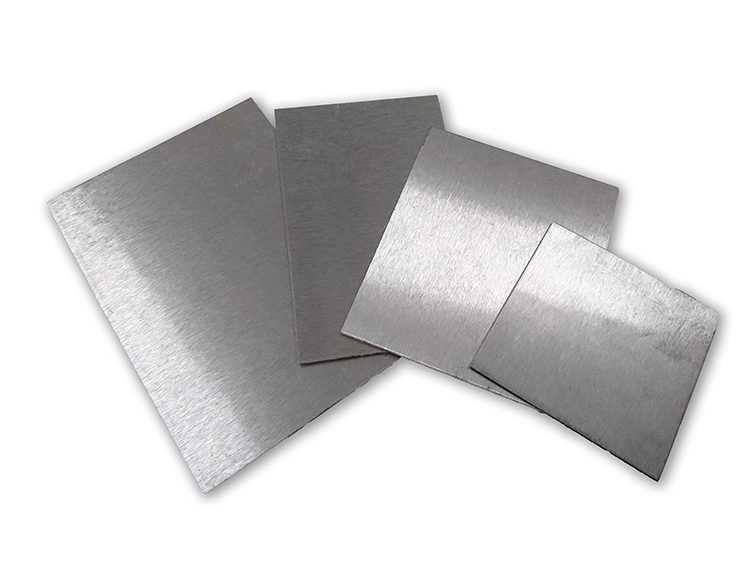

Magnesium alloy is a light metal structure material with high specific strength and specific stiffness and excellent machinability. In recent years, magnesium alloys have attracted widespread attention from countries all over the world. As promising lightweight materials, their research has attracted much attention, and a series of technologies have been developed to promote the use of magnesium alloys in transportation, aerospace, defense, and military industries. application.
With the continuous deepening of magnesium alloy research in my country, great progress has been made in magnesium alloy alloy design and plastic deformation technology research, and a series of magnesium alloys with high strength, thermal conductivity and heat resistance have been developed. High-strength magnesium alloys have partially replaced medium-strength aluminum alloys in aerospace, defense, and military applications.
1. High strength: The strength of magnesium alloy profiles are typically three times that of aluminum or equivalent steel alloys, which is why they are often chosen as a lightweight alternative.
2. Corrosion resistance:Magnesium alloys have excellent corrosion-resistance when exposed to environments with mild levels of salt or other corrosive elements, which makes them a good option for applications such as marine structures that may need to withstand frequent exposure to harsh environments.
3. Dimensional stability:Magnesium alloy profiles are less likely to warp or bend at higher temperatures, and are more dimensionally stable than other materials.
4. Durability: Magnesium alloy profiles are extremely durable, so they can be used in a wide range of applications and can withstand constant exposure to stress and other forces.
5. Thermal conductivity: Magnesium has a higher thermal conductivity than other metals, making it a good choice for applications such as heat sinks.
6. Weldability: Magnesium is relatively easy to weld and can be joined with other metals without special processes or techniques.